
The rising cost of education and the demand for specialized skills have pushed many to seek alternatives to traditional degrees. Enter employer funded bootcamp loans—a game-changing approach where companies invest in their employees’ upskilling by covering tuition for intensive, career-focused training programs. This isn’t just about filling skill gaps; it’s about building loyalty, fostering innovation, and preparing for a tech-driven future. In this article, we’ll dive deep into how these programs work, why companies are embracing them, and what they mean for employees and industries alike. Through original insights, case studies, historical context, and recent data, we’ll uncover why this trend is reshaping the modern workplace.
What Are Employer Funded Bootcamp Loans?
Imagine landing a job where your employer not only believes in your potential but also foots the bill for you to learn cutting-edge skills. That’s the essence of employer funded bootcamp loans. These programs involve companies partnering with coding bootcamps, data science academies, or other short-term training providers to cover tuition costs—fully or partially—for employees or new hires. In return, employees often commit to staying with the company for a set period or repay the loan through payroll deductions if they leave early.
Why Bootcamps Over Traditional Education?
Bootcamps are designed for speed and relevance. Unlike four-year degrees, which can cost upwards of $100,000 and take years to complete, bootcamps deliver practical skills in months—sometimes weeks. For example, a 2023 report by Course Report found that the average coding bootcamp costs $13,500 and takes 14 weeks, with 79% of graduates landing jobs in their field within six months. Companies see this as a win-win: they get skilled workers faster, and employees avoid crippling student debt.
How Do These Loans Work?
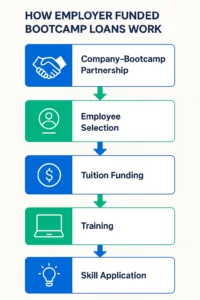
Typically, the process unfolds like this:
• Partnership: A company collaborates with a bootcamp, like Flatiron School or General Assembly’s employer partnerships to offer tailored training in AI or UX design.
• Selection: Employees or new hires are chosen based on role requirements or potential.
• Funding: The employer pays tuition upfront, sometimes as a loan forgiven over time with continued employment.
• Training: Participants attend rigorous courses, often part-time or online to balance work.
• Outcome: Graduates apply new skills to their roles, boosting productivity and innovation.
This model is gaining traction. A 2024 survey by LinkedIn revealed that 68% of companies with over 5,000 employees now offer some form of upskilling reimbursement, including bootcamp funding.
Why Companies Are Investing in Bootcamp Loans
The shift toward employer funded bootcamp loans isn’t just altruism—it’s strategic. As industries digitize, the skills gap widens. A 2024 World Economic Forum report estimated that 50% of all employees will need reskilling by 2030 due to automation and AI advancements. Companies are stepping up to bridge this gap, and here’s why.
Addressing the Talent Shortage
Tech roles like software engineering, cybersecurity, and data analysis are in high demand. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 22% growth in software developer jobs from 2020 to 2030—far outpacing the average for all occupations. Yet, universities can’t churn out graduates fast enough. Bootcamps fill this void, and companies funding them ensure a steady pipeline of talent.
Boosting Employee Retention
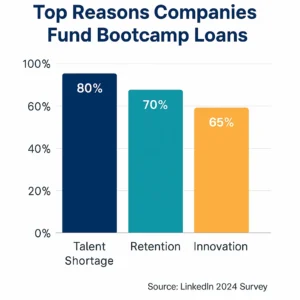
Paying for an employee’s education signals trust and commitment. In return, workers feel valued and are less likely to jump ship. A 2023 Gallup study found that employees who receive professional development are 3.5 times more likely to stay with their employer. For instance, Amazon’s Career Choice program, which covers bootcamp tuition, has retained 75% of participants for at least two years post-training.
Driving Innovation
Skilled employees drive progress. Take Google: its internal “Googler-to-Googler” training, paired with external bootcamp partnerships, has led to breakthroughs in AI and cloud computing. By upskilling workers, companies stay competitive in fast-evolving markets.
A Historical Perspective: Education as a Corporate Investment
The concept of employers funding education isn’t new—it’s been woven into the fabric of industry for centuries. Let’s step back to see how we got here.
The Industrial Era: Apprenticeships and Beyond
In the 19th century, apprenticeships were the norm. Blacksmiths, carpenters, and machinists trained under masters, often with room and board provided. Companies like Ford Motor Company later formalized this in the early 20th century, offering in-house schools to teach assembly line skills. By 1916, Ford’s training programs had upskilled thousands, boosting efficiency and loyalty.
The GI Bill and Corporate Buy-In
Post-World War II, the GI Bill of 1944 set a precedent for subsidized education. Companies took note, launching tuition reimbursement programs. IBM, for example, began covering college courses for employees in the 1950s, recognizing that educated workers fueled innovation. This laid the groundwork for today’s bootcamp loans.
The Tech Boom: A New Frontier
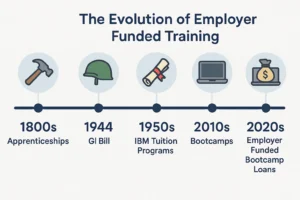
The dot-com era of the late 1990s accelerated demand for tech skills. Traditional education couldn’t keep up, birthing the first coding bootcamps in the early 2010s. Companies like AT&T, with its Workforce 2020 initiative launched in 2016, began funding bootcamps to retrain employees for digital roles. This marked a pivot from broad education to targeted upskilling.
Case Studies: Companies Leading the Charge
To understand the impact of employer funded bootcamp loans, let’s explore real-world examples. These stories highlight how companies and employees benefit.
Amazon: Career Choice Program
Launched in 2012, Amazon’s Career Choice covers up to 95% of tuition for courses, including bootcamps, in high-demand fields like software development. By 2024, over 100,000 employees had participated globally. Take Sarah, a warehouse worker in Ohio. After completing a web development bootcamp through Career Choice, she transitioned to a software engineering role at Amazon, doubling her salary. The program’s success lies in its flexibility—employees can pursue skills unrelated to their current role, fostering mobility.
Fact: Amazon invested $1.2 billion in upskilling programs from 2019 to 2024, with Career Choice graduates reporting a 30% higher job satisfaction rate.
Accenture: Future Talent Platform
Accenture’s Future Talent Platform partners with bootcamps like General Assembly to train employees in AI, cloud computing, and cybersecurity. In 2023, the company upskilled 250,000 workers, with 60% completing bootcamp-style programs. John, a project manager, learned data analytics through a sponsored course and led a $10 million client project leveraging his new skills. Accenture’s approach shows how bootcamps can transform mid-career professionals.
Fact: Accenture reported a 15% increase in project delivery efficiency after integrating bootcamp-trained employees.
Walmart: Live Better U
Walmart’s Live Better U, launched in 2018, offers tuition coverage for bootcamps and degrees. By 2024, 50,000 associates had enrolled, with 20% opting for tech bootcamps. Maria, a store associate, completed a UX design bootcamp and now designs internal tools for Walmart’s e-commerce platform. The program’s no-cost model (employees pay $1/day, later reimbursed) removes financial barriers.
Fact: Walmart’s retention rate for Live Better U participants is 20% higher than the company average.
The Employee Experience: Stories from the Ground
Beyond corporate strategy, employer funded bootcamp loans change lives. Let’s meet a few beneficiaries whose journeys illustrate the human side of this trend.
From Retail to Tech: Emma’s Transformation
Emma, 28, worked as a retail associate in Chicago. Her employer, a major retailer, offered a bootcamp loan program with App Academy. Nervous but determined, she enrolled in a 24-week coding course. “I was terrified I’d fail,” she recalls. “But the company’s support—mentors, study groups—kept me going.” Today, Emma’s a junior developer, earning 60% more. Her story shows how these programs empower career pivots.
Mid-Career Leap: Raj’s Reinvention
Raj, 42, was a marketing analyst facing obsolescence as AI reshaped his field. His employer’s partnership with DataCamp offered a sponsored data science bootcamp. “I went from spreadsheets to Python in six months,” he says. Now, Raj leads predictive analytics projects, proving it’s never too late to upskill.
The Numbers: Data Driving the Trend
Recent data underscores why employer funded bootcamp loans are booming. Here’s a snapshot:
• Demand for Skills: A 2024 McKinsey report found that 87% of executives face skill gaps, with tech skills topping the list, driving demand for employer funded bootcamp loans.
• Bootcamp Growth: The global bootcamp market is projected to reach $1.2 billion by 2027, growing at 13% annually (Statista, 2024).
• ROI for Companies: Firms investing in upskilling see a 21% increase in productivity, per a 2023 PwC study.
• Employee Impact: Bootcamp graduates earn 51% more on average post-training, according to a 2024 SwitchUp survey.
Breaking Down Costs
Bootcamp tuition ranges from $7,000 to $20,000, but employer sponsorship eliminates this burden. For context, the average student loan debt in the U.S. is $37,000 (Federal Reserve, 2024). By contrast, bootcamp loans, often forgiven over 2-3 years, offer a debt-free path to career growth.
Industry Adoption
Tech leads the charge, but other sectors are catching up. A 2024 SHRM survey found:
• Tech: 82% of companies offer bootcamp funding (e.g., Google, Microsoft).
• Finance: 65% (e.g., JPMorgan Chase).
• Retail: 45% (e.g., Target, Walmart).
• Healthcare: 30%, with growth in data analytics training.
Challenges and Criticisms
No initiative is flawless. Employer funded bootcamp loans face hurdles that deserve scrutiny.
Retention Agreements: A Double-Edged Sword
Many programs require employees to stay for 1-3 years post-training or repay the loan. While this ensures ROI for companies, it can feel restrictive. A 2023 HR Dive report noted that 15% of employees in such programs felt “trapped” by repayment clauses.
Accessibility Gaps
Not all workers qualify. Programs often prioritize high-potential employees or tech roles, leaving others—like entry-level or non-tech staff—out. A 2024 EdSurge study found that only 40% of sponsored bootcamp participants come from non-technical backgrounds.
Quality Concerns
Not all bootcamps deliver. A 2023 Consumer Reports investigation flagged some programs for outdated curricula or low job placement rates. Companies must vet partners carefully to avoid wasting resources.
A Unique Angle: Bootcamps as Cultural Catalysts
Here’s a fresh perspective: Employer funded bootcamp loans aren’t just about skills—they’re reshaping workplace culture. By investing in learning, companies foster environments of growth and adaptability. This cultural shift has ripple effects.
Building a Learning Ecosystem
Organizations like Salesforce use bootcamp partnerships to create “learning ecosystems.” Employees access ongoing training, from beginner coding to advanced AI. This normalizes continuous learning, making teams more resilient to change.
Empowering Diversity
Bootcamps can level the playing field. Companies like IBM target underrepresented groups for sponsored training, boosting diversity in tech. A 2024 TechCrunch report noted that 35% of bootcamp graduates are women or minorities, compared to 20% in traditional CS programs.
The Future of Employer Funded Bootcamp Loans
What’s next? The trend is accelerating, driven by tech advancements and workforce needs.
AI and Personalization
AI-driven bootcamps are emerging, tailoring curricula to individual learners. Companies like Microsoft are piloting AI-enhanced programs, with early results showing 25% faster skill acquisition (Forbes, 2024).
Expansion Beyond Tech
While tech dominates, sectors like healthcare and manufacturing are adopting bootcamps. For example, Kaiser Permanente funds nursing informatics training, blending clinical and tech skills.
Policy Support
Governments are taking note. In 2024, the U.S. Department of Labor launched a $100 million grant for employer-led training, including bootcamps. This could scale corporate investment further.
Frequently Asked Questions About Employer Funded Bootcamp Loans
Wondering how employer funded bootcamp loans can transform your career? We’ve rounded up the most common questions to guide you through this exciting opportunity. Let’s dive in.
What Are Employer Funded Bootcamp Loans?
Unlike private bootcamp loans, Employer funded bootcamp loans let companies pay for your training in skills like coding or data analytics, often through partnerships with bootcamps like Flatiron School. Instead of taking on debt, you might commit to staying with the employer for a few years. For example, Sarah, a warehouse worker, became a developer through Amazon’s program, which covered 95% of her tuition. These deals can be forgiven over time, making them a smart way to upskill.
Why Do Companies Pay for Bootcamp Tuition?
Companies fund bootcamps to tackle skill shortages—87% of leaders see gaps in tech talent (McKinsey, 2024). They also boost retention; trained employees are 3.5 times more likely to stay (Gallup, 2023). Plus, upskilled workers drive results, like Accenture’s 15% efficiency gains from trained teams. By investing in employer funded bootcamp loans, firms build stronger, future-ready workforces.
Which Companies Offer Employer Funded Coding Bootcamps?
SHRM’s 2024 survey shows 82% of tech firms offer employer funded coding bootcamps, followed by finance (65%) and retail (45%).
Big names lead the charge:
1. Amazon: Funds tech training via Career Choice.
2. Accenture: Offers AI and cloud bootcamps.Walmart: Covers UX and data courses through Live Better U.
3. Microsoft: Supports cybersecurity programs. Smaller tech firms are jumping in, too. Check career pages or ask HR about employer funded coding bootcamp options.
What Are the Risks of Employer Funded Bootcamp Loans?
There’s a catch sometimes. You might need to stay 1-3 years or repay the loan if you leave early—15% of workers feel stuck by this (HR Dive, 2023). Not everyone qualifies; programs often favor tech roles. Also, some bootcamps have shaky outcomes, so vet their placement rates. Employer funded bootcamp loans are powerful, but read the fine print.
How Do I Find Jobs Offering Bootcamp Loans?
Look for companies like Walmart or IBM on job boards like LinkedIn, using filters like “upskilling” or “tuition benefits.” Browse their websites for terms like “employer funded training.” Network with professionals in tech or retail, where these programs thrive. Focus on roles needing skills like coding, as they’re more likely to offer bootcamp loans.
Will a Bootcamp Loan Guarantee a Better Job?
No promises, but the odds are good. Graduates earns 51% more on average (SwitchUp, 2024), and 79% land field-related jobs within six months (Course Report, 2023). Take Raj, who went from analyst to data lead after his company’s bootcamp. Your success hinges on applying new skills and aligning with your employer’s needs—chat with your boss first.
Conclusion: A Win for All
Employer funded bootcamp loans are more than a perk—they’re a revolution in how we learn and work. Companies gain skilled, loyal talent; employees unlock new careers without debt; and industries stay agile in a digital age. As we’ve seen through history, case studies, and data, this model builds on a legacy of corporate investment in people. Yet, it’s not without challenges—accessibility and quality must improve to maximize impact.
For workers, the message is clear: seek employers who invest in your growth. For companies, it’s a call to action: upskill or fall behind. As Emma, Raj, and countless others show, these programs don’t just change careers—they change lives.
