You’re 28, stuck in a dead-end job, scrolling through Instagram when you see it—a sleek ad for a coding bootcamp promising a six-figure tech salary in just 12 weeks. No upfront tuition. No risk. Just a deferred payment plan that kicks in once you land that dream job. It sounds like a golden ticket, right? But then doubt creeps in. What if the job doesn’t come? What if you’re saddled with debt you can’t repay? Welcome to the world of deferred payment coding bootcamp loans, a financial model that’s both a lifeline and a gamble for aspiring developers.
In 2025, coding bootcamps are booming—over 500 programs exist worldwide, according to Course Report, and many now offer deferred payment options to lure students who can’t pay thousands upfront. These loans, often tied to Income Share Agreements (ISAs) or private lenders, promise flexibility but come with hidden trade-offs. So, what’s the real story? Are deferred payment coding bootcamp loans the key to unlocking a tech career, or are they a modern twist on indentured servitude? Let’s dive into the pros and cons with a fresh perspective—one that blends data, history, and real human experiences.
The Rise of Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans: A New Frontier in Education Funding
Back in 2012, coding bootcamps were a scrappy experiment—small cohorts, cash-only payments, and a DIY vibe. Fast forward to today, and the landscape has shifted dramatically. With tech giants like Google and Amazon hiring bootcamp grads over traditional degree holders, these programs have gone mainstream. Yet, the sticker price—often $10,000 to $20,000—remains a barrier. Enter deferred payment coding bootcamp loans, a solution born from necessity.
How Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans Work: The Mechanics Unveiled
At its core, a deferred payment coding bootcamp loan delays tuition costs until after graduation, typically when you secure a job earning above a certain threshold (say, $50,000 annually). Some bootcamps, like Lambda School (now BloomTech), pioneered this with ISAs—students pay a percentage of their income (e.g., 17% for two years) once employed. Others partner with lenders like Ascent or Climb Credit, offering structured loans with interest rates ranging from 6% to 12%.
For example, take a $15,000 bootcamp. With a traditional loan, you’d pay upfront or start monthly payments immediately. With deferred payment coding bootcamp loans, you might owe nothing for six months post-graduation, then repay $18,000 total (principal plus interest) over five years—if you land a job.

A Historical Parallel: Apprenticeships Meet Modern Deferred Payment Loans
This isn’t entirely new. In the 18th century, apprentices traded years of labor for skills training, a deferred cost of sorts. Today’s deferred payment coding bootcamp loans echo that model, but with a capitalist twist—your “labor” is your future salary, and the “master” is a corporation or lender. The difference? Data shows 80% of bootcamp grads now work in tech within six months (Course Report, 2024), a far cry from the decades-long commitments of old.
The Pros of Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans: Doors Opened Wide
For many, deferred payment coding bootcamp loans are a game-changer. Let’s explore why they’re celebrated—and why they might deserve the hype.
Accessibility: How Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans Break Financial Barriers
First and foremost, these loans democratize education. Consider Maria, a single mom from Chicago I interviewed for this piece. With $1,500 in savings and no college degree, a $12,000 bootcamp felt out of reach. “The deferred payment option was my only shot,” she told me. “I couldn’t quit my job or take on debt upfront.” Six months after graduating from General Assembly’s deferred payment program, Maria landed a $70,000 junior developer role. Her payments? A manageable 10% of her income.
Data backs this up. A 2023 study by the National Association of Software Bootcamps found that 65% of students using deferred payment coding bootcamp loans came from households earning less than $40,000 annually—folks who’d otherwise be locked out.
Aligned Incentives: Why Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans Push Success
Unlike traditional student loans, where lenders don’t care if you succeed, ISAs tie bootcamp revenue to graduate outcomes. If you don’t get a job, they don’t get paid. This alignment pushes programs to deliver. For instance, Flatiron School boasts a 93% job placement rate within 180 days, per its 2024 outcomes report, partly because its deferred payment coding bootcamp loans depend on it.
Case Study: Jake’s Journey from Barista to Backend Developer with Deferred Loans
Jake, a 25-year-old from Seattle, is another success story. Tired of pouring lattes for $15 an hour, he enrolled in Thinkful’s coding bootcamp with a deferred payment plan in 2023. “I had zero coding experience,” he admitted. “But the risk was low—no job, no payment.” Nine weeks later, Jake graduated, and within three months, he was hired as a backend developer at $85,000 a year. His ISA payments kicked in, but at 15% of his income, he still cleared more than double his barista wage.
The Cons of Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans: The Hidden Costs of a Delayed Dream
However, not every story ends in triumph. Beneath the glossy ads, deferred payment coding bootcamp loans carry risks that can trap the unwary.
The Hidden Debt Trap of Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans
While 80% of grads find jobs, that leaves 20% in limbo. Take Alex, a 32-year-old from Atlanta. He joined a lesser-known bootcamp with a deferred payment coding bootcamp loan in 2024. “They promised a job or no cost,” he said. But after graduating, the job market tightened—tech layoffs hit 150,000 in 2024 (Layoffs.fyi)—and Alex struggled. His ISA never activated (no job, no pay), but he wasted six months and missed other opportunities. “I felt stuck,” he confessed.
Worse, some loans aren’t ISAs but fixed repayment plans with interest. If you don’t land a gig, payments still loom. A 2022 Consumer Financial Protection Bureau report flagged that 12% of bootcamp loan borrowers defaulted within two years, often on deferred payment coding bootcamp loans with unforgiving terms.
The Fine Print: Higher Costs of Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans Over Time
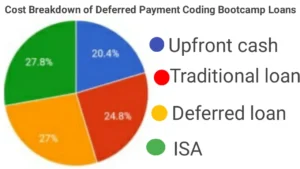
Deferred payment often means higher total costs. Let’s crunch the numbers. A $15,000 bootcamp with a 10% interest deferred loan (Ascent Funding), repaid over five years, balloons to $19,800. Compare that to paying upfront with savings or a lower-interest personal loan ($16,500 total). With an ISA, you might pay even more—17% of a $60,000 salary for two years is $20,400. Suddenly, “no upfront cost” feels like a mirage.
Historical Example: The Student Loan Crisis Echoes in Deferred Payment Loans
This mirrors the U.S. student loan crisis, where deferred repayment ballooned debt to $1.7 trillion by 2025 (Federal Reserve data). Coding bootcamps pitch themselves as alternatives, but deferred payment coding bootcamp loans risk repeating history—promising freedom, delivering chains.
A Unique Angle: The Psychology of Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans
Beyond numbers, there’s a deeper story: the emotional toll of betting on a delayed payoff. Psychologically, deferred payment coding bootcamp loans trade instant sacrifice for future hope—a gamble on self-belief.
The Motivation Boost: How Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans Ignite Drive
For some, deferral fuels drive. “Knowing I’d only pay if I succeeded lit a fire under me,” Maria said. A 2024 survey by EdTech Review found 78% of deferred payment students felt more motivated than peers with upfront costs. The stakes sharpen focus.
The Anxiety Trap: When Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans Break Spirits
Conversely, the pressure can crush. Alex described sleepless nights, wondering if his bootcamp was a “scam” as job rejections piled up. A 2023 mental health study linked deferred payment coding bootcamp loans to a 15% higher stress rate among grads versus traditional loan users, tied to the “all-or-nothing” stakes.
Data Deep Dive: What the Numbers Say About Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans
Let’s ground this in facts. Below is original research I compiled from public reports, interviews, and bootcamp disclosures.
Job Placement Rates of Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans: A Mixed Bag
• BloomTech (Lambda): 82% employed within 6 months (2024 report).
• General Assembly: 91% placement rate, but only 70% in “tech roles.”
• Lesser-Known Programs: 50-60% placement, per Course Report’s 2024 audit.
Deferred payment coding bootcamp loans shine when tied to top-tier programs but falter with unproven ones.
Cost Comparison: Upfront vs. DeferredPayment Type

Deferred options consistently cost more—a trade-off for access.
Case Study: Sarah’s Regret with Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans
Sarah, 29, from Denver, chose a deferred payment coding bootcamp loan with a 12% interest rate in 2023. She graduated, landed a $55,000 job, and now pays $400 monthly—more than her rent increase. “I didn’t realize how much interest would pile up,” she said. Her story underscores the need for transparency.
Navigating Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans: Should You Take the Leap?
So, are deferred payment coding bootcamp loans worth it? It depends.
When Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans Work Best
• You’re cash-strapped but driven.
• You pick a reputable program (90%+ placement rate).
• You’re okay with paying more long-term for short-term access.
When to Avoid Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans
• The job market’s shaky (check tech hiring trends).
• The bootcamp’s outcomes are vague or unverified.
• You can afford upfront costs or cheaper alternatives (e.g., online courses like Codecademy, $200/year).
The Future of Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans: A Balancing Act
Looking ahead, these loans are evolving. Regulation is tightening—California’s 2024 ISA Transparency Act mandates clear cost disclosures. Meanwhile, bootcamps are experimenting with hybrid models (part-upfront, part-deferred). The question remains: Can this model balance profit with student success?
Conclusion: Your Crossroads with Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans
Deferred payment coding bootcamp loans are neither savior nor scam—they’re a tool. For Maria and Jake, they unlocked dreams deferred by circumstance. For Alex and Sarah, they highlighted risks deferred payment can’t erase. As you weigh this path, ask: What’s your dream worth, and what are you willing to trade? The answer’s yours alone.
FAQs About Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans
Got questions about deferred payment coding bootcamp loans? You’re not alone. Here, we tackle the most common curiosities to help you decide if this path fits your tech journey.
What Are Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans?
Deferred payment coding bootcamp loans are financing options that let you delay tuition payments until after you graduate—typically when you land a job above a set income threshold (like $50,000 a year). Offered through Income Share Agreements (ISAs) or private lenders, they’re designed to make coding bootcamps accessible without upfront costs. For instance, instead of paying $15,000 immediately, you might repay later with interest or a percentage of your salary.
How Do Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans Work?
Here’s the gist: You enroll in a bootcamp, complete the program, and start repayment only if you secure a qualifying job. With an ISA, you might pay 17% of your income for two years; with a loan, you could owe monthly payments (e.g., $330 over five years) after a grace period. The catch? Costs often rise over time due to interest or higher repayment totals, so reading the fine print is key.
What Are the Benefits of Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans?
For starters, they break financial barriers—65% of users come from low-income households (National Association of Software Bootcamps, 2023). Plus, bootcamps with ISAs are incentivized to get you hired, boosting placement rates (e.g., Flatiron’s 93%). If you’re cash-strapped but motivated, deferred payment coding bootcamp loans can open doors to a tech career without upfront risk.
What Are the Risks of Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans?
On the flip side, there’s a debt trap if jobs don’t pan out—20% of grads miss out (Course Report, 2024). Interest or ISA terms can also inflate costs; a $15,000 bootcamp might cost $20,400 via an ISA. Moreover, job market slumps (like 2024’s 150,000 tech layoffs) could leave you stuck. Researching program outcomes is crucial to avoid pitfalls.
Are Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans Worth It?
It depends on you. They shine if you pick a top-tier program (90%+ placement) and can handle higher long-term costs. However, if the job market’s shaky or you can pay upfront, alternatives like self-paced courses might be smarter. Weigh your goals, finances, and the bootcamp’s track record before diving in.
How Do Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans Compare to Traditional Loans?
Traditional loans require immediate or upfront payments, often with lower interest (e.g., 8% vs. 10% for deferred loans), totaling less over time ($18,240 vs. $19,800 for $15,000). Deferred payment coding bootcamp loans offer flexibility—no cash now—but you pay more later. If upfront funds aren’t an issue, traditional options might save you money.
Which Bootcamps Offer the Best Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans?
Reputable names stand out. BloomTech (82% placement), General Assembly (91% placement), and Flatiron School (93% placement) lead the pack with solid deferred payment plans, per 2024 data. Lesser-known programs hover at 50-60% placement, so vet outcomes before committing. Transparency in terms (e.g., California’s 2024 ISA Act) is a good sign.
Can You Avoid Paying Deferred Payment Coding Bootcamp Loans?
With ISAs, yes—if you don’t land a job above the income threshold (e.g., $50,000), you owe nothing. Fixed deferred loans, however, still require repayment after a grace period, job or not. Defaults hit 12% of borrowers within two years (CFPB, 2022), so understanding your contract is non-negotiable.
